|
It is a health disorder in women that occurs when cells in the lining of the uterus (womb) grows in other areas of the body. This can lead to pain , irregular bleeding , and problems getting pregnant.
It is a disease difficult to diagnose , however early treatment avoids complications.

Causes
Each month, woman's ovaries produce hormones that tell the cells lining the uterus to swell and become thicker . The body eliminates these foreign cells of the uterine lining (endometrium ) when you would get your period . If these cells , called endometrial cells implant and grow outside the uterus , endometriosis results .
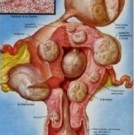
The tumors are called endometrial tissue implants . Women with endometriosis typically have tissue implants on the ovaries , bowel , rectum , bladder, and in the lining of the pelvic area. They can also occur in other areas of the body. Unlike the endometrial cells are found in the uterus , implants outside the uterus tissue remain in place when it is the menstrual period . They sometimes bleed a little and grow if you have the following period . This ongoing process leads to pain and other symptoms of endometriosis.
The cause of endometriosis is unknown. One theory is that the endometrial cells shed during menstruation returned through the fallopian tubes into the pelvis, where they implant and multiply. This is called retrograde menstruation. This retrograde menstrual flow occurs in many women , but researchers think the immune system may be different in women with endometriosis.
Endometriosis is common and sometimes can be hereditary. Although endometriosis is typically diagnosed between ages 20 and 35, the condition probably begins about the time of onset of regular menstruation . It is more common in people with hypothyroidism.
A woman who has a mother or sister with endometriosis are more likely to develop this disease than other women.
You are more likely to develop endometriosis if:
• began menstruation at an early age .
• Never had children.
• Have frequent periods or lasting 7 days or more .
• Has a closed hymen , which blocks the flow of blood during the menstrual period.
Symptoms
Menstrual pain is the main symptom of endometriosis. 
• Painful periods ( Algomenorrea ) . Sometimes the patient leaves his work for pain or even to faint.
• Low before and during menstruation abdominal pain.
• Cramps a week or two before and during menstruation ( cramps may be permanent and can be dull or severe ) .
• Pain during or after sexual intercourse.
• Pelvic pain or low back pain that can occur at any time during the menstrual cycle.
Note : You may not manifest any symptoms . Some women with a large number of endometriotic implants in the pelvis not no pain , while some with mild disease have severe pain.
Exams and Tests
• Pelvic exam
• Endovaginal ultrasound .
• Laparoscopy ( Gold Standard ) can be performed only by the SILS port
• Laboratory determination of antigen Ca 125
Treatment
Treatment depends on the following factors:
• Age
• Severity of symptoms .
• Severity of illness .
• Whether or not you want children in the future .
Treatment options include:
• Medications to control pain .
• hormonal medications to prevent the worsening of endometriosis.
• Progesterone .
• gonadotropin agonists such as goserelin and leuprolide acetate to prevent the ovaries to produce estrogen and create a condition similar to menopause . Side effects include hot flashes, vaginal dryness and changes in mood. The treatment usually is limited to six months because it can lead to loss of bone density. In some cases, it can be extended for up to one year .
Surgery may be recommended if you have severe pain that does not improve with other treatments which can include:
• Laparoscopy or laparotomy to diagnose endometriosis and remove all implants and scar tissue (adhesions ) .
• Hysterectomy to remove the uterus (womb) if you have severe symptoms and do not want children in the future. You can also remove one or both ovaries and fallopian tubes.
Hormone therapy and laparoscopy can not cure endometriosis , but these treatments can partially or completely relieve symptoms in many patients for years . Rarely , endometriosis may recur . Dependent on the stage at which the disease is found.
Complications
Endometriosis can lead to problems getting pregnant (infertility ) . Not all women , especially those with mild endometriosis, will have infertility. Laparoscopy to remove adhesions related condition may help improve your chances of getting pregnant.
Other complications of endometriosis include:
• Prolonged or chronic pelvic pain that interferes with social and work activities.
• Large cysts in the pelvis (called endometriomas ) that may break .
In a few cases , endometriosis implants may cause blockages of the gastrointestinal or urinary tracts , but is uncommon.
Very rarely , cancer can develop in the areas of endometriosis after menopause .

References
Lobo R. Endometriosis: etiology , pathology , diagnosis, management.
In: Katz VL , Lentz GM, Lobo RA , Gershenson DM . Comprehensive Gynecology. 5th ed . Philadelphia , Pa : Mosby Elsevier , 2007 : chap . 19 .
Brown J , Pan A, Hart RJ . Gonadotrophin -releasing hormone analogues for pain Associated with endometriosis. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2010 Dec 8; ( 12): CD008475 .
Giudice LC . Clinical practice . Endometriosis . N Engl J Med 2010 Jun 24; 362 (25) :2389-98 .
Ziegler D , Borghese B, Chapron C. Endometriosis and infertility : pathophysiology and management. Lancet . 2010 Aug 28 , 376 (9742) :730-8 . ACOG Practice Bulletin No. 110: noncontraceptive uses of hormonal contraceptives . Obstet Gynecol . 2010 Jan , 115 (1) :206-18 .
Dr. Benjamin Gloria Avila Endometriosis
|